India’s Foreign Trade: 2009-10 (April-January)* This article reviews India’s merchandise trade performance during 2009-10 (April- January) on the basis of data released by the Directorate General of Commercial Intelligence and Statistics (DGCI&S); disaggregated commodity-wise details for the period April-August 2009 are also analysed. Highlights
-
India’s merchandise exports during January 2010 at US$ 14.3 billion recorded a growth of 11.5 per cent as compared with a decline of 13.6 per cent registered in January 2009. The decline in exports which began since October 2008 continued for twelve consecutive months. The exports turned around by exhibiting an increase of 0.3 per cent in October 2009 and the positive growth in exports continued thereafter (monthly average growth of 13.0 per cent during November 2009 to January 2010). This trend indicated stability in positive growth in exports.
-
During 2009-10 (April-January) exports stood at US$ 131.8 billion, posting a decline of 17.9 per cent as against a growth of 22.8 per cent during the corresponding period of 2008-09.
-
Imports during January 2010 at US$ 24.7 billion showed a high growth of 35.5 per cent as against a decline of 20.2 per cent recorded in January 2009. This was due to growth in both petroleum, oil and lubricants (POL) and non-POL imports. After a continuous decline for one year, imports had turned around in December 2009 by exhibiting an increase of 27.2 per cent. The positive growth in imports continued in January 2010.
-
During 2009-10 (April-January), imports at US$ 218.1 billion recorded a decline of 19.8 per cent as against a growth of 32.0 per cent a year ago.
-
Petroleum, oil and lubricants (POL) imports at US$ 63.9 billion during 2009- 10 (April-January) showed a decline of 25.4 per cent, as against a high growth of 36.1 per cent a year ago, primarily due to reduction in international crude oil prices over the period. The average price of Indian basket of crude oil during 2009-10 (April-January) stood at US$ 68.4 per barrel (ranged between US$ 50.1 – 77.4 per barrel), which was lower by 24.3 per cent than US$ 90.3 per barrel (ranged between US$ 40.6 – 132.5 per barrel) during 2008-09 (April-January).
-
Non-POL imports during 2009-10 (April- January) at US$ 154.3 billion showed a fall of 17.3 per cent as against a growth of 30.2 per cent a year ago.
-
Trade deficit during 2009-10 (April- January) amounted to US$ 86.3 billion, thereby showing a decline of US$ 25.3 billion (22.6 per cent) over US$ 111.6 billion during 2008-09 (April-January), mainly due to decline in both oil and non-oil imports.
India’s Merchandise Trade during 2009-10 (April-January) Exports India’s merchandise exports during January 2010 at US$ 14.3 billion recorded a growth of 11.5 per cent as compared with a decline of 13.6 per cent registered in January 2009 (Statement 1). The decline in exports which began since October 2008 continued for twelve consecutive months. The rates of decline in exports showed persistent moderation since June 2009 and in October 2009, exports turned around by exhibiting an increase of 0.3 per cent. The positive growth in exports continued thereafter (monthly average growth of 13.0 per cent during November 2009 to January 2010). Also, the increase in exports was consistent with the uptrend in world commodity prices. All this indicated stability in improved performance of exports (Chart 1). Cumulatively, exports during 2009-10 (April January) stood at US$ 131.8 billion, posting a decline of 17.9 per cent as against a growth of 22.8 per cent during 2008-09 (April- January) [Table 1 and Statement 2].
 |
Table 1: India's Merchandise Trade: April-January |
(US $ billion) |
Items |
2008-09 R |
2009-10 P |
April-January |
1 |
2 |
3 |
Exports |
|
160.4 |
|
131.8 |
|
|
(22.8) |
|
(-17.9) |
Oil Exports |
24.0 |
|
.. |
|
|
(9.5) |
|
|
|
Non-Oil Exports |
136.4 |
|
.. |
|
|
(25.5) |
|
|
|
Imports |
|
272.0 |
|
218.1 |
|
|
(32.0) |
|
(-19.8) |
Oil Imports |
85.6 |
|
63.9 |
|
|
(36.1) |
|
(-25.4) |
|
Non-Oil Imports |
186.4 |
|
154.3 |
|
|
(30.2) |
|
(-17.3) |
|
Trade Balance |
|
-111.6 |
|
-86.3 |
Oil Trade Balance |
-61.6 |
|
.. |
|
Non-Oil Trade Balance |
-50.0 |
|
.. |
|
R : Revised. P : Provisional. .. Not available.
Note : Figures in parentheses show percentage change over the corresponding period of the previous year.
Source : Compiled from Ministry of Commerce and Industry and DGCI&S data. |
The commodity-wise exports data released by DGCI&S for April-August 2009 revealed that manufactured goods maintained the largest share at 70.0 per cent, followed by primary products (13.4 per cent) and petroleum products (13.0 per cent). Moreover, the share of manufactured goods has increased along with decrease in the shares of petroleum products and primary products (Table 2). During April-August 2009, exports of all major commodity groups declined (Statement 3). Exports of primary products during April-August 2009 showed a sharp decline of 34.1 per cent as against a high growth of 52.6 per cent a year ago, due to decline in its major components. Within primary products, agricultural and allied products exports at US$ 6.1 billion showed a decline of 32.5 per cent (growth of 62.4 per cent during the corresponding period of previous year). This was due to decline in most of its components. Exports of ores and minerals declined by 37.9 per cent as against a growth of 33.8 per cent a year ago, mainly due to decline in iron ore and processed minerals.
Table 2: India's Exports of Principal Commodities |
(Percentage Shares) |
Commodity Group |
2007-08 |
2008-09 |
2008-09 |
2009-10 |
April- |
March |
April-August |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
I. |
Primary Products |
16.9 |
13.7 |
13.9 |
13.4 |
|
Agriculture and Allied Products |
11.3 |
9.5 |
9.7 |
9.6 |
|
Ores and Minerals |
5.6 |
4.2 |
4.2 |
3.8 |
II. |
Manufactured Goods |
63.2 |
66.5 |
64.2 |
70.0 |
|
Leather and Manufactures |
2.2 |
1.9 |
1.8 |
2.1 |
|
Chemicals and Related Products |
13.0 |
12.3 |
11.3 |
13.1 |
|
Engineering Goods |
22.9 |
25.5 |
24.8 |
24.1 |
|
Textiles and Textile Products |
11.9 |
10.8 |
9.8 |
12.4 |
|
Gems and Jewellery |
12.1 |
15.1 |
15.7 |
17.3 |
III. |
Petroleum Products |
17.4 |
14.5 |
17.4 |
13.0 |
IV. |
Others |
2.5 |
5.3 |
4.5 |
3.6 |
|
Total Exports |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
Source: Compiled from DGCI&S data. |
Exports of manufactured goods during April-August 2009 at US$ 44.6 billion exhibited a decline of 25.4 per cent in contrast with a high growth of 49.6 per cent a year ago, due to decline in its major components. Within manufactured goods, exports of engineering goods at US$ 15.3 billion declined by 33.6 per cent against a high growth of 61.9 per cent a year ago. This was due to decline in all its major constituents such as machinery and instruments, manufacture of metals, transport equipments and electronic goods as also iron and steel. Gems and jewellery exports during April-August 2009 at US$ 11.0 billion recorded a sharp decline of 24.7 per cent as against a high growth of 84.4 per cent during the corresponding period of the previous year. Chemicals and related products exports during April-August 2009 at US$ 8.4 billion showed a decline of 20.8 per cent (a growth of 33.9 per cent during April-August 2008). The decline in the exports of chemicals and related products was led by fall in exports of its largest component, viz., ‘basic chemicals, pharmaceuticals and cosmetics’ as also in other components. Exports of textiles and textile products during April-August 2009 at US$ 7.9 billion exhibited a decline of 13.4 per cent as against a growth of 17.0 per cent a year ago. This was because of decline in the exports of its major components such as readymade garments and cotton yarn, fabrics, made-ups. Exports of petroleum products at US$ 8.3 billion during April-August 2009 registered a decline of 48.8 per cent as against a growth of 52.5 per cent a year ago. This occurred in the aftermath of sharp decline in world oil prices during April-August 2009 over April- August 2008 (Chart 3). The volume of these exports declined by 0.9 per cent during the period as compared with a decline of 10.9 per cent during April-August 2008. Destination-wise, during April-August 2009, among the regions, developing countries and OECD countries were the major markets for India’s exports with these groups accounting for 37.5 per cent and 36.6 per cent shares, respectively (Table 3). Another major contributor was OPEC with the share of 23.5 per cent. During April- August 2009, the shares of OECD and OPEC increased while that of developing countries declined. Country-wise, the UAE was the largest destination in April-August 2009, with a share of 14.4 per cent in India’s total exports. It was followed by the US (11.2 per cent), China (5.2 per cent), Singapore (4.5 per cent), Hong Kong (4.1 per cent), the UK (3.8 per cent), the Netherlands (3.5 per cent) and Germany (3.2 per cent). Direction of India’s exports during April-August 2009 indicated that exports to all major markets, such as the EU, OPEC and developing countries declined (Statement 4). Imports Imports during January 2010 at US$ 24.7 billion showed a high growth of 35.5 per cent as against a decline of 20.2 per cent recorded in January 2009. This was due to growth in both petroleum, oil and lubricants (POL) and non-POL imports (Statement 1).
Table 3: India’s Exports to Principal Regions |
(Percentage Shares) |
Region/Country |
2007-08 |
2008-09 |
2008-09 |
2009-10 |
April- |
March |
April-August |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
I. |
OECD Countries |
39.5 |
36.9 |
35.3 |
36.6 |
|
EU |
21.2 |
21.0 |
20.2 |
20.4 |
|
North America |
13.5 |
12.1 |
11.3 |
12.0 |
|
US |
12.7 |
11.3 |
10.6 |
11.2 |
|
Asia and Oceania |
3.2 |
2.5 |
2.3 |
2.9 |
|
Other OECD Countries |
1.6 |
1.4 |
1.5 |
1.4 |
II. |
OPEC |
16.6 |
21.0 |
22.6 |
23.5 |
III. |
Eastern Europe |
1.1 |
1.1 |
1.1 |
1.0 |
IV. |
Developing Countries |
42.5 |
37.0 |
38.1 |
37.5 |
|
Asia |
31.6 |
27.7 |
28.1 |
28.3 |
|
SAARC |
5.9 |
4.6 |
4.7 |
4.7 |
|
Other Asian Developing Countries |
25.7 |
23.1 |
23.5 |
23.6 |
|
Africa |
7.5 |
6.2 |
6.6 |
6.5 |
|
Latin America |
3.4 |
3.1 |
3.4 |
2.7 |
V. |
Others / Unspecified |
0.3 |
4.0 |
2.9 |
1.4 |
|
Total Exports |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
Source: Compiled from DGCI&S data. |
Imports started falling since December 2008 but witnessed consistently lower rates of decline since September 2009 (Chart 1). After a continuous decline for one year, imports turned around in December 2009 by exhibiting an increase of 27.2 per cent. The positive growth in imports continued in January 2010. During 2009-10 (April- January) imports at US$ 218.1 billion registered a decline of 19.8 per cent (32.0 per cent growth a year ago) [Table 1 and Statement 2]. POL imports at US$ 63.9 billion during 2009-10 (April-January) showed a decline of 25.4 per cent, as against a high growth of 36.1 per cent a year ago, primarily due to reduction in international crude oil prices over the period. The average price of Indian basket of crude oil during 2009-10 (April-January) stood at US$ 68.4 per barrel (ranged between US$ 50.1 – 77.4 per barrel), which was lower by 24.3 per cent than US$ 90.3 per barrel (ranged between US$ 40.6 – 132.5 per barrel) during 2008-09 (April-January) (Table 4). Non-POL imports at US$ 154.3 billion recorded a fall of 17.3 per cent during 2009-10 (April-January) as against a growth of 30.2 per cent in 2008-09 (April-January). The commodity-wise imports data for April-August 2009 indicated that POL imports at US$ 30.9 billion showed a decline of 42.5 per cent as against a high growth of 86.6 per cent a year ago, mainly due to sharp reduction in international crude oil prices over the period (Statement 5). The volume of POL imports, however, showed a growth of 12.1 per cent as against a growth of 8.7 per cent a year ago.
Table 4: Trends in Crude Oil Prices |
(US $/barrel) |
Period |
Dubai |
Brent |
WTI* |
Indian Basket** |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
2000-01 |
25.9 |
28.1 |
30.3 |
26.8 |
2001-02 |
21.8 |
23.2 |
24.1 |
22.4 |
2002-03 |
25.9 |
27.6 |
29.2 |
26.6 |
2003-04 |
26.9 |
29.0 |
31.4 |
27.8 |
2004-05 |
36.4 |
42.2 |
45.0 |
39.2 |
2005-06 |
53.4 |
58.0 |
59.9 |
55.7 |
2006-07 |
60.9 |
64.4 |
64.7 |
62.4 |
2007-08 |
77.3 |
82.4 |
82.3 |
79.5 |
2008-09 |
82.1 |
84.7 |
85.8 |
82.7 |
January 2009 |
45.0 |
44.9 |
41.7 |
44.0 |
January 2010 |
76.6 |
76.4 |
78.4 |
76.6 |
* West Texas Intermediate.
** The composition of Indian basket of crude represents average of Oman and Dubai for sour grades and Brent (dated) for sweet grade in the ratio of 63.5:36.5 w.e.f. April 1, 2009.
Sources: International Monetary Fund, International Financial Statistics; World Bank’s Commodity Price Pink Sheet for February 2010; Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas, Government of India. |
Non-POL imports during April-August 2009 at US$ 72.9 billion witnessed a decline of 27.2 per cent as against a high growth of 38.6 per cent during the corresponding period of 2008. Slowdown in non-POL imports was mainly due to sharp decline in imports of capital goods (decline of 25.9 per cent as against a growth of 58.3 per cent in April-August 2008), gold and silver (fall of 19.1 per cent as against a growth of 10.1 per cent during April-August 2008), pearls, precious and semi-precious stones (fall of 41.2 per cent as against a growth of 99.5 per cent during April-August 2008), fertilisers, chemicals, iron and steel, coal, coke and briquettes and metalliferrous ores and metal scrap. However, imports of edible oil and pulses showed substantial growth. During April-August 2009 the shares of capital goods, gold and silver, organic and inorganic chemicals, coal, coke and briquettes, and iron and steel in total imports went up, while those of petroleum, crude and products, pearls, precious and semi-precious stones and fertilisers came down (Table 5). Source-wise, during April-August 2009, developing countries had the highest share in India’s total imports (34.2 per cent), followed by OECD countries (32.7 per cent) and OPEC (30.1 per cent) [Table 6]. The shares of developing countries and OECD countries increased, while that of OPEC declined during the period. Country-wise, China continued to be the single largest source of imports with the share of 12.0 per cent in total imports, followed by the US (6.1 per cent), the UAE (5.8 per cent), Saudi Arabia (5.7 per cent), Australia (4.4 per cent), Iran (4.4 per cent), Switzerland (4.1 per cent) and Germany (3.9 per cent). Direction of India’s imports during April-August 2009 indicated that imports from all the major regions declined (Statement 6).
Table 5: Imports of Principal Commodities |
(Percentage Shares) |
Commodity/Group |
2007-08 |
2008-09 |
2008-09 |
2009-10 |
April-March |
April-August |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
1. Petroleum, Crude and Products |
31.7 |
30.1 |
34.9 |
29.8 |
2. Capital Goods |
27.9 |
23.6 |
21.5 |
23.6 |
3. Gold and Silver |
7.1 |
7.2 |
7.7 |
9.3 |
4. Organic and Inorganic Chemicals |
3.9 |
4.0 |
4.3 |
4.6 |
5. Coal, Coke and Briquettes, etc. |
2.6 |
3.3 |
3.0 |
3.2 |
6. Fertilisers |
2.2 |
4.5 |
4.1 |
2.4 |
7. Metalliferrous Ores, Metal Scrap, etc. |
3.1 |
2.6 |
2.7 |
2.7 |
8. Iron and Steel |
3.5 |
3.1 |
2.7 |
3.2 |
9. Pearls, Precious and Semi-Precious Stones |
3.2 |
5.5 |
5.2 |
4.5 |
10. Others |
14.8 |
16.1 |
13.9 |
16.7 |
Total Imports |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
Source: Compiled from DGCI&S data. |
Table 6: Shares of Groups/Countries in India’s Imports |
(Percentage Shares) |
Region/Country |
2007-08 |
2008-09 |
2008-09 |
2009-10 |
April-March |
April-August |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
I. OECD Countries |
35.4 |
31.7 |
30.6 |
32.7 |
EU |
15.3 |
13.9 |
13.1 |
13.6 |
France |
2.5 |
1.5 |
1.4 |
1.2 |
Germany |
3.9 |
3.9 |
3.5 |
3.9 |
UK |
2.0 |
1.9 |
1.7 |
1.7 |
North America |
9.1 |
6.9 |
6.2 |
6.8 |
US |
8.4 |
6.1 |
5.5 |
6.1 |
Asia and Oceania |
5.8 |
6.3 |
5.9 |
7.1 |
Other OECD Countries |
5.2 |
4.6 |
5.4 |
5.3 |
II. OPEC |
30.7 |
32.1 |
36.3 |
30.1 |
III. Eastern Europe |
1.5 |
2.2 |
2.0 |
2.3 |
IV. Developing Countries |
31.5 |
31.9 |
30.7 |
34.2 |
Asia |
25.5 |
25.9 |
25.0 |
27.2 |
SAARC |
0.8 |
0.6 |
0.6 |
0.6 |
Other Asian Developing Countries |
24.7 |
25.3 |
24.4 |
26.6 |
of which: |
|
|
|
|
People’s Republic of China |
10.8 |
10.6 |
10.2 |
12.0 |
Africa |
3.7 |
4.1 |
4.1 |
4.6 |
Latin America |
2.3 |
1.9 |
1.6 |
2.4 |
V. Others / Unspecified |
0.9 |
2.1 |
0.4 |
0.7 |
Total Imports |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
Source: Compiled from DGCI&S data. |
Trade Deficit Trade deficit during 2009-10 (April- January) amounted to US$ 86.3 billion, which was lower by US$ 25.3 billion (22.6 per cent) than US$ 111.6 billion a year ago, due to relatively larger decline in imports than exports during the period (Statement 2 and Chart 1). Trade deficit on oil account during April-August 2009 stood at US$ 22.6 billion, which was lower by US$ 15.0 billion than US$ 37.6 billion a year ago. Trade deficit on non-oil account during this period amounted to US$ 17.6 billion, which was lower by US$ 5.6 billion than US$ 23.2 billion in April-August 2008. Global Trade World merchandise exports which declined since November 2008 as an outcome of global economic crisis, started recovering consistently since May 2009 with reduction in the rates of decline and turned around in November 2009. According to the latest monthly data from International Monetary Fund’s (IMF) International Financial Statistics (IFS), in November 2009 the world exports showed a positive growth of 5.5 per cent. This was in line with the rise in world commodity prices. There has been strong convergence among the world exports and the exports of advanced economies and emerging and developing economies since May 2009 (Chart 2). Cumulatively, world merchandise exports during January-November 2009, in dollar terms, showed a decline of 22.9 per cent as against a growth of 18.2 per cent a year ago (Table 7). During the same period, exports of advanced economies declined by 23.9 per cent in contrast with a growth of 13.3 per cent a year back, and the exports of emerging and developing economies declined by 21.8 per cent as against a growth of 27.2 per cent a year ago.
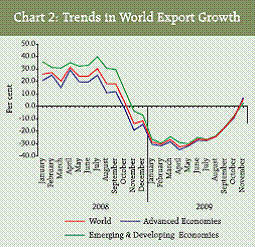 |
Table 7: Growth in Exports – Global Scenario |
(Per cent) |
Region/Country |
2007 |
2008 |
2008 |
2009 |
January-December |
January-November |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
World |
|
14.1 |
|
15.8 |
|
18.2 |
|
-22.9 |
Advanced Economies |
|
13.5 |
|
11.0 |
|
13.3 |
|
-23.9 |
US |
12.0 |
|
11.9 |
|
14.4 |
|
-20.1 |
|
France |
12.3 |
|
10.1 |
|
11.9 |
|
-26.4* |
|
Germany |
18.0 |
|
10.8 |
|
11.8 |
|
-24.5 |
|
Japan |
7.8 |
|
12.3 |
|
14.0 |
|
-29.1 |
|
Emerging and Developing Economies |
|
15.3 |
|
24.6 |
|
27.2 |
|
-21.8 |
Singapore |
10.1 |
|
13.0 |
|
16.3 |
|
-23.4 |
|
China |
25.6 |
|
17.3 |
|
19.4 |
|
-18.7 |
|
India |
23.3 |
|
29.7 |
|
29.7** |
|
-19.3** |
|
Indonesia |
14.7 |
|
24.4 |
|
20.8 |
|
-13.3 |
|
Korea |
14.1 |
|
13.6 |
|
21.5 |
|
-18.6 |
|
Malaysia |
9.6 |
|
19.1 |
|
16.7 |
|
-17.1 |
|
Thailand |
17.1 |
|
12.9 |
|
16.7 |
|
-24.2 |
|
* : January-October 2009 over January-October 2008.
** : January-December over corresponding period of previous year.
Sources: 1. IMF (www.imfstatistics.org).
2. DGCI&S for India. |
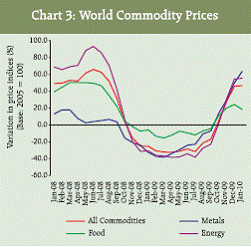
World Commodity Prices According to IMF’s IFS, the world commodity prices which started falling since October 2008 witnessed substantially higher rates of decline during subsequent months. However, the rates of decline in prices progressively moderated since August 2009 and the commodity prices, in fact, showed a rise since November 2009. In January 2010, the commodity prices showed a rise of 41.0 per cent (Chart 3). During this month, the prices of energy, food and metals increased by 50.8 per cent, 10.2 per cent and 59.6 per cent, respectively.
 |
Statement 1 : India’s Foreign Trade - January 2010
|
Year |
Exports |
Imports |
Trade Balance |
Total |
Oil |
Non-Oil |
Total |
Oil |
Non-Oil |
Total |
Oil |
Non-Oil |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
|
Rupees crore
|
2007-08 |
58,624 |
9,425 |
49,199 |
89,947 |
33,487 |
56,460 |
-31,323 |
-24,062 |
-7,261 |
|
(20.6) |
(48.8) |
(16.4) |
(40.4) |
(101.0) |
(19.1) |
|
|
|
2008-09 R |
62,844 |
6,028 |
56,816 |
89,015 |
20,561 |
68,454 |
-26,171 |
-14,533 |
-11,638 |
|
(7.2) |
(-36.0) |
(15.5) |
(-1.0) |
(-38.6) |
(21.2) |
|
|
|
2009-10 P |
65,920 |
.. |
.. |
113,545 |
32,415 |
81,130 |
-47,625 |
.. |
.. |
|
(4.9) |
|
|
(27.6) |
(57.7) |
(18.5) |
|
|
|
|
US dollar million
|
2007-08 |
14,889 |
2,394 |
12,495 |
22,844 |
8,505 |
14,339 |
-7,955 |
-6,111 |
-1,844 |
|
(35.8) |
(67.5) |
(31.0) |
(58.1) |
(126.3) |
(34.1) |
|
|
|
2008-09 R |
12,869 |
1,234 |
11,635 |
18,228 |
4,522 |
13,706 |
-5,359 |
-3,288 |
-2,071 |
|
(-13.6) |
(-48.4) |
(-6.9) |
(-20.2) |
(-46.8) |
(-4.4) |
|
|
|
2009-10 P |
14,343 |
.. |
.. |
24,705 |
7,053 |
17,652 |
-10,362 |
.. |
.. |
|
(11.5) |
|
|
(35.5) |
(56.0) |
(28.8) |
|
|
|
P : Provisional. R : Revised. .. Not available.
Note : Figures in brackets relate to percentage variation over the corresponding period of the previous year.
Source : Press Note, Ministry of Commerce & Industry. |
Statement 2 : India’s Foreign Trade |
Year |
Exports |
Imports |
Trade Balance |
Total |
Oil |
Non-Oil |
Total |
Oil |
Non-Oil |
Total |
Oil |
Non-Oil |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
April-March |
Rupees crore |
2006-07 |
571,779 |
84,520 |
487,259 |
840,506 |
258,572 |
581,935 |
-268,727 |
-174,052 |
-94,675 |
|
(25.3) |
(64.0) |
(20.3) |
(27.3) |
(32.8) |
(24.9) |
|
|
|
2007-08 R |
655,864 |
114,192 |
541,672 |
1,012,312 |
320,655 |
691,657 |
-356,448 |
-206,463 |
-149,985 |
|
(14.7) |
(35.1) |
(11.2) |
(20.4) |
(24.0) |
(18.9) |
|
|
|
2008-09 P |
840,755 |
123,398 |
717,357 |
1,374,435 |
419,946 |
954,489 |
-533,680 |
-296,548 |
-237,132 |
|
(28.2) |
(8.1) |
(32.4) |
(35.8) |
(31.0) |
(38.0) |
|
|
|
US dollar million |
2006-07 |
126,414 |
18,635 |
107,780 |
185,735 |
56,945 |
128,790 |
-59,321 |
-38,311 |
-21,010 |
|
(22.6) |
(60.1) |
(17.9) |
(24.5) |
(29.5) |
(22.4) |
|
|
|
2007-08 R |
162,904 |
28,363 |
134,541 |
251,439 |
79,645 |
171,795 |
-88,535 |
-51,281 |
-37,254 |
|
(28.9) |
(52.2) |
(24.8) |
(35.4) |
(39.9) |
(33.4) |
|
|
|
2008-09 P |
185,295 |
26,830 |
158,466 |
303,696 |
91,306 |
212,390 |
-118401 |
-64476 |
-53925 |
|
(13.7) |
(-5.4) |
(17.8) |
(20.8) |
(14.6) |
(23.6) |
|
|
|
April-January |
Rupees crore |
2007-08 |
525,757 |
88,344 |
437,413 |
830,027 |
253,385 |
576,642 |
-304,270 |
-165,040 |
-139,229 |
|
(12.2) |
(23.3) |
(10.2) |
(18.4) |
(16.9) |
(19.1) |
|
|
|
2008-09 R |
715,764 |
108,388 |
607,376 |
1,215,214 |
376,884 |
838,330 |
-499,450 |
-268,496 |
-230,954 |
|
(36.1) |
(22.7) |
(38.9) |
(46.4) |
(48.7) |
(45.4) |
|
|
|
2009-10 P |
629,224 |
.. |
.. |
1,041,513 |
304,942 |
736,571 |
-412,289 |
.. |
.. |
|
(-12.1) |
|
|
(-14.3) |
(-19.1) |
(-12.1) |
|
|
|
US dollar million |
2007-08 |
130,657 |
21,929 |
108,728 |
206,146 |
62926 |
143,220 |
-75,489 |
-40,997 |
-34,492 |
|
(26.9) |
(39.5) |
(24.6) |
(33.8) |
(28.5) |
(36.2) |
|
|
|
2008-09 R |
160,438 |
24,010 |
136,428 |
272,037 |
85,623 |
186,414 |
-111,599 |
-61,613 |
-49,986 |
|
(22.8) |
(9.5) |
(25.5) |
(32.0) |
(36.1) |
(30.2) |
|
|
|
2009-10 P |
131,776 |
.. |
.. |
218,120 |
63,863 |
154,257 |
-86,344 |
.. |
.. |
|
(-17.9) |
|
|
(-19.8) |
(-25.4) |
(-17.3) |
|
|
|
P : Provisional. R : Revised. .. : Not available.
Note : 1. Figures in brackets relate to percentage variation over the corresponding period of the previous year.
2. Data conversion has been done using period average exchange rates.
Source : Press Note, Ministry of Commerce & Industry. |
Statement 3 : India’s Exports of Principal Commodities |
(US$ million) |
Commodity/Group |
April-August |
Percentage Variation |
2007-08 |
2008-09 R |
2009-10 P |
(3)/(2) |
(4)/(3) |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
I. |
Primary Products |
8,457.6 |
12,908.3 |
8,501.9 |
52.6 |
-34.1 |
|
|
(13.9) |
(13.9) |
(13.4) |
|
|
|
A. Agricultural & Allied Products |
5,556.3 |
9,025.6 |
6,092.0 |
62.4 |
-32.5 |
|
of which : |
(9.1) |
(9.7) |
(9.6) |
|
|
|
1. Tea |
167.4 |
249.0 |
208.0 |
48.8 |
-16.5 |
|
2. Coffee |
177.1 |
248.5 |
166.0 |
40.3 |
-33.2 |
|
3. Rice |
974.7 |
1,206.8 |
1,233.3 |
23.8 |
2.2 |
|
4. Wheat |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
— |
— |
|
5. Cotton Raw incl. Waste |
236.0 |
388.9 |
237.2 |
64.8 |
-39.0 |
|
6. Tobacco |
188.1 |
309.7 |
368.8 |
64.7 |
19.1 |
|
7. Cashew incl. CNSL |
217.4 |
332.0 |
244.9 |
52.7 |
-26.2 |
|
8. Spices |
519.9 |
670.3 |
474.2 |
28.9 |
-29.3 |
|
9. Oil Meal |
333.3 |
1,067.9 |
527.6 |
220.4 |
-50.6 |
|
10.Marine Products |
646.1 |
595.8 |
577.4 |
-7.8 |
-3.1 |
|
11.Sugar & Molasses |
526.5 |
870.0 |
11.8 |
65.2 |
-98.6 |
|
B. Ores & Minerals |
2,901.3 |
3,882.7 |
2,409.9 |
33.8 |
-37.9 |
|
of which : |
(4.8) |
(4.2) |
(3.8) |
|
|
|
1. Iron Ore |
1,536.5 |
2,290.6 |
1,435.0 |
49.1 |
-37.4 |
|
2. Processed Minerals |
529.7 |
695.2 |
496.9 |
31.2 |
-28.5 |
II. |
Manufactured Goods |
39,964.1 |
59,767.9 |
44,559.3 |
49.6 |
-25.4 |
|
of which : |
(65.5) |
(64.2) |
(70.0) |
|
|
|
A. Leather & Manufactures |
1,428.3 |
1,706.4 |
1,342.3 |
19.5 |
-21.3 |
|
B. Chemicals & Related Products |
7,879.5 |
10,552.4 |
8,359.4 |
33.9 |
-20.8 |
|
1. Basic Chemicals, Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics |
5,167.8 |
7,054.9 |
5,786.1 |
36.5 |
-18.0 |
|
2. Plastic & Linoleum |
1,266.8 |
1,565.0 |
1,199.6 |
23.5 |
-23.4 |
|
3. Rubber, Glass, Paints & Enamels, etc. |
1,126.2 |
1,400.1 |
1,012.5 |
24.3 |
-27.7 |
|
4. Residual Chemicals & Allied Products |
318.7 |
532.5 |
361.2 |
67.1 |
-32.2 |
|
C. Engineering Goods |
14,249.0 |
23,074.9 |
15,332.0 |
61.9 |
-33.6 |
|
of which : |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. Manufactures of Metals |
2,519.0 |
3,426.8 |
2,339.1 |
36.0 |
-31.7 |
|
2. Machinery & Instruments |
3,424.0 |
5,019.9 |
3,725.9 |
46.6 |
-25.8 |
|
3. Transport Equipments |
2,634.0 |
5,231.3 |
4,423.9 |
98.6 |
-15.4 |
|
4. Iron & Steel |
2,271.8 |
3,611.5 |
1,099.6 |
59.0 |
-69.6 |
|
5. Electronic Goods |
1,237.3 |
2,979.7 |
2,447.2 |
140.8 |
-17.9 |
|
D. Textiles and Textile Products |
7,767.7 |
9,086.9 |
7,872.4 |
17.0 |
-13.4 |
|
1. Cotton Yarn, Fabrics, Made-ups, etc. |
1,790.6 |
2,005.0 |
1,263.1 |
12.0 |
-37.0 |
|
2. Natural Silk Yarn, Fabrics Madeups, etc. (incl.silk waste) |
156.8 |
171.7 |
120.7 |
9.5 |
-29.7 |
|
3. Manmade Yarn, Fabrics, Made-ups, etc. |
1,104.1 |
1,443.9 |
1,434.3 |
30.8 |
-0.7 |
|
4. Manmade Staple Fibre |
90.5 |
140.2 |
118.2 |
55.0 |
-15.7 |
|
5. Woollen Yarn, Fabrics, Madeups, etc. |
35.1 |
46.6 |
36.2 |
32.9 |
-22.3 |
|
6. Readymade Garments |
4,028.9 |
4,677.1 |
4,477.2 |
16.1 |
-4.3 |
|
7. Jute & Jute Manufactures |
128.4 |
156.9 |
94.1 |
22.2 |
-40.1 |
|
8. Coir & Coir Manufactures |
62.1 |
68.1 |
65.5 |
9.7 |
-3.7 |
|
9. Carpets |
371.2 |
377.4 |
263.1 |
1.7 |
-30.3 |
|
(a) Carpet Handmade |
363.8 |
374.1 |
259.3 |
2.9 |
-30.7 |
|
(b) Carpet Millmade |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
— |
— |
|
(c) Silk Carpets |
7.4 |
3.3 |
3.9 |
-55.9 |
18.0 |
|
E. Gems & Jewellery |
7,904.5 |
14,574.8 |
10,978.3 |
84.4 |
-24.7 |
|
F. Handicrafts |
209.7 |
135.5 |
78.2 |
-35.4 |
-42.3 |
III. |
Petroleum Products |
10,599.3 |
16,167.8 |
8,284.0 |
52.5 |
-48.8 |
|
|
(17.4) |
(17.4) |
(13.0) |
0.0 |
-25.0 |
IV. |
Others |
2,016.4 |
4,273.6 |
2,272.6 |
111.9 |
-46.8 |
|
|
(3.3) |
(4.6) |
(3.6) |
|
|
Total Exports |
61,037.4 |
93,117.7 |
63,617.7 |
52.6 |
-31.7 |
P : Provisional. R : Revised.
Note : Figures in brackets relate to percentage to total exports for the period.
Source : DGCI&S. |
Statement 4 : Direction of India’s Foreign Trade- Exports |
(US$ million) |
Group/Country |
April-August |
Percentage Variation |
2007-08 |
2008-09 R |
2009-10 P |
(3)/(2) |
(4)/(3) |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
I. |
O E C D Countries |
24,614.9 |
32,850.2 |
23,299.8 |
33.5 |
-29.1 |
A. |
E U |
13,204.0 |
18,782.9 |
12,980.6 |
42.3 |
-30.9 |
|
of which: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. Belgium |
1,751.0 |
2,272.7 |
1,308.0 |
29.8 |
-42.4 |
|
2. France |
1,000.2 |
1,421.4 |
1,182.1 |
42.1 |
-16.8 |
|
3. Germany |
1,989.7 |
2,941.5 |
2,012.5 |
47.8 |
-31.6 |
|
4. Italy |
1,584.5 |
1,916.6 |
1,220.2 |
21.0 |
-36.3 |
|
5. Netherlands |
1,666.0 |
3,018.1 |
2,216.3 |
81.2 |
-26.6 |
|
6. U K |
2,561.9 |
3,069.2 |
2,403.3 |
19.8 |
-21.7 |
B. |
North America |
8,652.3 |
10,506.7 |
7,604.9 |
21.4 |
-27.6 |
|
1. Canada |
499.2 |
609.0 |
455.8 |
22.0 |
-25.2 |
|
2. U S A |
8,153.13 |
9,897.62 |
7,149.14 |
21.4 |
-27.8 |
C. |
Asia and Oceania |
1,790.9 |
2,146.9 |
1,839.5 |
19.9 |
-14.3 |
|
of which: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. Australia |
416.3 |
674.0 |
477.9 |
61.9 |
-29.1 |
|
2. Japan |
1,320.4 |
1,380.9 |
1,238.5 |
4.6 |
-10.3 |
D. |
Other O E C D Countries |
967.7 |
1,413.7 |
874.8 |
46.1 |
-38.1 |
|
Of which: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. Switzerland |
242.3 |
366.3 |
196.0 |
51.2 |
-46.5 |
II. |
O P E C |
10,972.0 |
21,076.2 |
14,964.6 |
92.1 |
-29.0 |
|
of which: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. Indonesia |
688.6 |
1,338.0 |
1,331.3 |
94.3 |
-0.5 |
|
2. Iran |
1,094.1 |
1,255.1 |
875.6 |
14.7 |
-30.2 |
|
3. Iraq |
80.3 |
226.6 |
218.4 |
182.2 |
-3.6 |
|
4. Kuwait |
266.8 |
373.0 |
316.7 |
39.8 |
-15.1 |
|
5. Saudi Arabia |
1,384.7 |
2,996.3 |
1,636.2 |
116.4 |
-45.4 |
|
6. U A E |
6,405.3 |
13,330.5 |
9,182.1 |
108.1 |
-31.1 |
III. |
Eastern Europe |
667.8 |
1,030.3 |
629.5 |
54.3 |
-38.9 |
|
of which: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. Russia |
342.3 |
586.1 |
344.0 |
71.2 |
-41.3 |
IV. |
Developing Countries |
24,231.4 |
35,492.8 |
23,842.5 |
46.5 |
-32.8 |
|
of which: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
A. Asia |
17,457.2 |
26,188.9 |
17,997.5 |
50.0 |
-31.3 |
|
a) S A A R C |
3,111.3 |
4,341.6 |
2,979.5 |
39.5 |
-31.4 |
|
1. Afghanistan |
90.8 |
150.1 |
212.2 |
65.4 |
41.4 |
|
2. Bangladesh |
820.4 |
1,281.6 |
842.9 |
56.2 |
-34.2 |
|
3. Bhutan |
33.6 |
49.5 |
38.7 |
47.5 |
-22.0 |
|
4. Maldives |
32.9 |
51.8 |
31.4 |
57.4 |
-39.4 |
|
5. Nepal |
518.0 |
721.8 |
510.7 |
39.3 |
-29.3 |
|
6. Pakistan |
662.2 |
732.7 |
650.4 |
10.7 |
-11.2 |
|
7. Sri Lanka |
953.4 |
1,354.0 |
693.3 |
42.0 |
-48.8 |
|
b) Other Asian Developing Countries |
14,346.0 |
21,847.3 |
15,018.1 |
52.3 |
-31.3 |
|
of which: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. People’s Republic of China |
3,155.1 |
4,423.0 |
3,288.1 |
40.2 |
-25.7 |
|
2. Hong Kong |
2,338.6 |
3,017.2 |
2,611.9 |
29.0 |
-13.4 |
|
3. South Korea |
934.3 |
1,619.2 |
1,036.6 |
73.3 |
-36.0 |
|
4. Malaysia |
780.1 |
1,309.1 |
1,210.2 |
67.8 |
-7.6 |
|
5. Singapore |
2,559.1 |
5,020.7 |
2,880.9 |
96.2 |
-42.6 |
|
6. Thailand |
624.1 |
1,066.6 |
592.1 |
70.9 |
-44.5 |
|
B. Africa |
4,902.7 |
6,175.8 |
4,103.9 |
26.0 |
-33.5 |
|
of which: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. Benin |
87.9 |
87.9 |
74.2 |
0.0 |
-15.6 |
|
2. Egypt Arab Republic |
537.3 |
975.0 |
484.4 |
81.5 |
-50.3 |
|
3. Kenya |
446.2 |
765.6 |
650.9 |
71.6 |
-15.0 |
|
4. South Africa |
1,105.5 |
926.9 |
871.6 |
-16.2 |
-6.0 |
|
5. Sudan |
151.9 |
214.2 |
172.1 |
41.1 |
-19.7 |
|
6. Tanzania |
226.2 |
598.1 |
390.9 |
164.4 |
-34.6 |
|
7. Zambia |
67.5 |
46.7 |
32.9 |
-30.8 |
-29.6 |
|
C. Latin American Countries |
1,871.5 |
3,128.1 |
1,741.1 |
67.1 |
-44.3 |
V. |
Others |
442.2 |
242.1 |
244.0 |
-45.3 |
0.8 |
VI. |
Unspecified |
109.2 |
2,426.2 |
637.3 |
— |
-73.7 |
Total Exports |
61,037.4 |
93,117.7 |
63,617.7 |
52.6 |
-31.7 |
P : Provisional. R : Revised.
Source : DGCI & S. |
Statement 5 : India’s Imports of Principal Commodities |
(US$ million) |
Commodity/Group |
April-August |
Percentage Variation |
2007-08 |
2008-09 R |
2009-10 P |
(3)/(2) |
(4)/(3) |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
I. Bulk Imports |
42,459.5 |
75,989.3 |
44,931.4 |
79.0 |
-40.9 |
|
(42.0) |
(49.4) |
(43.3) |
|
|
A. Petroleum, Petroleum Products |
28,798.00 |
53,741.29 |
30,888.23 |
86.6 |
-42.5 |
& Related Material |
(28.5) |
(34.9) |
(29.8) |
|
|
B. Bulk Consumption Goods |
1,800.5 |
1,616.5 |
2,846.9 |
-10.2 |
76.1 |
1. Wheat |
21.2 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
— |
— |
2. Cereals & Cereal Preparations |
14.1 |
18.0 |
17.4 |
28.1 |
-3.2 |
3. Edible Oil |
1,249.3 |
1,131.2 |
1,927.8 |
-9.5 |
70.4 |
4. Pulses |
515.2 |
466.7 |
635.6 |
-9.4 |
36.2 |
5. Sugar |
0.8 |
0.6 |
266.1 |
— |
— |
C. Other Bulk Items |
11,861.0 |
20,631.6 |
11,196.3 |
73.9 |
-45.7 |
1. Fertilisers |
1,816.8 |
6,251.8 |
2,513.4 |
244.1 |
-59.8 |
a) Crude |
176.5 |
415.1 |
271.1 |
135.2 |
-34.7 |
b) Sulphur & Unroasted Iron Pyrites |
80.7 |
462.2 |
38.3 |
472.8 |
-91.7 |
c) Manufactured |
1,559.6 |
5,374.4 |
2,204.0 |
244.6 |
-59.0 |
2. Non-Ferrous Metals |
1,328.2 |
4,302.2 |
1,275.3 |
223.9 |
-70.4 |
3. Paper, Paperboard & Mgfd. incl. Newsprint |
588.2 |
807.2 |
573.2 |
37.2 |
-29.0 |
4. Crude Rubber, incl. Synthetic & Reclaimed |
308.4 |
458.6 |
399.9 |
48.7 |
-12.8 |
5. Pulp & Waste Paper |
316.3 |
371.6 |
311.2 |
17.5 |
-16.3 |
6. Metalliferrous Ores & Metal Scrap |
3,635.2 |
4,225.2 |
2,807.5 |
16.2 |
-33.6 |
7. Iron & Steel |
3,867.9 |
4,215.0 |
3,315.8 |
9.0 |
-21.3 |
II. Non-Bulk Imports |
58,571.1 |
77,870.5 |
58,856.5 |
33.0 |
-24.4 |
|
(58.0) |
(50.6) |
(56.7) |
|
|
A. Capital Goods |
20,876.9 |
33,045.9 |
24,493.3 |
58.3 |
-25.9 |
1. Manufactures of Metals |
826.0 |
1,435.2 |
939.8 |
73.8 |
-34.5 |
2. Machine Tools |
810.1 |
1,156.6 |
649.4 |
42.8 |
-43.8 |
3. Machinery except Electrical & Electronics |
6,814.7 |
10,438.3 |
7,979.8 |
53.2 |
-23.6 |
4. Electrical Machinery except Electronics |
955.5 |
1,819.3 |
1,264.4 |
90.4 |
-30.5 |
5. Electronic Goods incl. Computer Software |
8,497.3 |
11,332.4 |
9,484.5 |
33.4 |
-16.3 |
6. Transport Equipments |
2,443.7 |
5,569.7 |
2,344.4 |
127.9 |
-57.9 |
7. Project Goods |
529.6 |
1,294.4 |
1,831.0 |
144.4 |
41.5 |
B. Mainly Export Related Items |
9,268.6 |
16,107.5 |
10,821.1 |
73.8 |
-32.8 |
1. Pearls, Precious & Semi-Precious Stones |
3,993.1 |
7,968.1 |
4,683.5 |
99.5 |
-41.2 |
2. Chemicals, Organic & Inorganic |
4,067.5 |
6,577.6 |
4,761.2 |
61.7 |
-27.6 |
3. Textile Yarn, Fabric, etc. |
1,008.4 |
1,216.6 |
1,053.8 |
20.6 |
-13.4 |
4. Cashew Nuts, raw |
199.6 |
345.2 |
322.6 |
73.0 |
-6.5 |
C. Others |
28,425.6 |
28,717.1 |
23,542.3 |
1.0 |
-18.0 |
of which : |
|
|
|
|
|
1. Gold & Silver |
10,780.9 |
11,873.8 |
9,601.9 |
10.1 |
-19.1 |
2. Artificial Resins & Plastic Materials |
1,463.1 |
1,989.2 |
2,033.3 |
36.0 |
2.2 |
3. Professional Instruments etc. except electrical |
1,512.1 |
1,929.5 |
1,541.5 |
27.6 |
-20.1 |
4. Coal, Coke & Briquettes etc. |
2,372.8 |
4,568.5 |
3,326.1 |
92.5 |
-27.2 |
5. Medicinal & Pharmaceutical Products |
704.7 |
866.9 |
841.9 |
23.0 |
-2.9 |
6. Chemical Materials & Products |
639.7 |
1,047.5 |
922.7 |
63.7 |
-11.9 |
7. Non-Metallic Mineral Manufactures |
380.7 |
558.7 |
429.7 |
46.8 |
-23.1 |
Total Imports |
101,030.6 |
153,859.8 |
103,787.9 |
52.3 |
-32.5 |
Memo Items |
Non-Oil Imports |
72,232.6 |
100,118.5 |
72,899.7 |
38.6 |
-27.2 |
Non-Oil Imports excl. Gold & Silver |
61,451.6 |
88,244.7 |
63,297.8 |
43.6 |
-28.3 |
Mainly Industrial Inputs* |
56,579.5 |
79,324.3 |
56,705.4 |
40.2 |
-28.5 |
P : Provisional. R : Revised.
* : Non oil imports net of gold and silver, bulk consumption goods, manufactured fertilisers and professional instruments.
Note: Figures in brackets relate to percentage to total imports for the period.
Source : DGCI & S. |
Statement 6 : Direction of India’s Foreign Trade- Imports |
(US$ million) |
Group / Country |
April-August |
Percentage Variation |
2007-08 |
2008-09 R |
2009-10 P |
(3)/(2) |
(4)/(3) |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
I. |
O E C D Countries |
33,145.8 |
47,092.5 |
33,978.2 |
42.1 |
-27.8 |
|
A. E U |
13,739.0 |
20,168.2 |
14,116.2 |
46.8 |
-30.0 |
|
of which: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. Belgium |
2,198.1 |
2,813.6 |
2,117.9 |
28.0 |
-24.7 |
|
2. France |
950.9 |
2,120.4 |
1,193.7 |
123.0 |
-43.7 |
|
3. Germany |
3,659.2 |
5,422.0 |
4,028.6 |
48.2 |
-25.7 |
|
4. Italy |
1,392.4 |
2,255.6 |
1,423.9 |
62.0 |
-36.9 |
|
5. Netherlands |
656.9 |
980.3 |
659.2 |
49.2 |
-32.8 |
|
6. U K |
2,105.6 |
2,636.6 |
1,803.6 |
25.2 |
-31.6 |
|
B. North America |
6,033.2 |
9,534.5 |
7,031.4 |
58.0 |
-26.3 |
|
1. Canada |
675.4 |
1,075.8 |
732.5 |
59.3 |
-31.9 |
|
2. U S A |
5,357.80 |
8,458.61 |
6,298.90 |
57.9 |
-25.5 |
|
C. Asia and Oceania |
6,546.2 |
9,018.3 |
7,355.1 |
37.8 |
-18.4 |
|
of which: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. Australia |
3,934.0 |
5,017.3 |
4,539.2 |
27.5 |
-9.5 |
|
2. Japan |
2,472.2 |
3,845.9 |
2,610.6 |
55.6 |
-32.1 |
|
D. Other O E C D Countries |
6,827.4 |
8,371.6 |
5,475.5 |
22.6 |
-34.6 |
|
of which: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. Switzerland |
5,769.8 |
6,928.2 |
4,248.8 |
20.1 |
-38.7 |
II. |
O P E C |
28,469.0 |
55,858.0 |
31,272.3 |
96.2 |
-44.0 |
|
of which: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. Indonesia |
2,016.0 |
2,616.3 |
3,225.3 |
29.8 |
23.3 |
|
2. Iran |
3,918.5 |
6,789.4 |
4,517.1 |
73.3 |
-33.5 |
|
3. Iraq |
2,228.6 |
4,685.3 |
2,526.4 |
110.2 |
-46.1 |
|
4. Kuwait |
2,579.2 |
5,175.3 |
2,999.6 |
100.7 |
-42.0 |
|
5. Saudi Arabia |
6,443.9 |
11,547.9 |
5,916.7 |
79.2 |
-48.8 |
|
6. U A E |
5,333.8 |
13,705.4 |
6,030.2 |
157.0 |
-56.0 |
III. |
Eastern Europe |
1,512.4 |
3,094.2 |
2,403.1 |
104.6 |
-22.3 |
|
of which: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. Russia |
839.6 |
1,973.3 |
1,498.8 |
135.0 |
-24.0 |
IV. |
Developing Countries |
31,585.3 |
47,266.4 |
35,467.4 |
49.6 |
-25.0 |
|
of which: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
A. Asia |
25,066.8 |
38,451.1 |
28,232.0 |
53.4 |
-26.6 |
|
a) S A A R C |
674.6 |
881.6 |
589.1 |
30.7 |
-33.2 |
|
1. Afghanistan |
22.4 |
32.4 |
27.9 |
44.5 |
-13.9 |
|
2. Bangladesh |
121.0 |
145.0 |
92.6 |
19.8 |
-36.1 |
|
3. Bhutan |
77.2 |
77.6 |
54.6 |
0.6 |
-29.7 |
|
4. Maldives |
1.5 |
2.1 |
0.7 |
42.6 |
-69.2 |
|
5. Nepal |
158.4 |
236.3 |
183.7 |
49.2 |
-22.3 |
|
6. Pakistan |
109.5 |
216.6 |
96.9 |
97.8 |
-55.3 |
|
7. Sri Lanka |
184.5 |
171.4 |
132.7 |
-7.1 |
-22.5 |
|
b) Other Asian Developing Countries |
24,392.3 |
37,569.5 |
27,642.8 |
54.0 |
-26.4 |
|
Of which: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. People’s Republic of China |
10,461.3 |
15,747.4 |
12,443.3 |
50.5 |
-21.0 |
|
2. Hong Kong |
1,126.4 |
2,584.1 |
1,418.2 |
129.4 |
-45.1 |
|
3. South Korea |
2,339.9 |
3,914.9 |
3,054.5 |
67.3 |
-22.0 |
|
4. Malaysia |
2,487.6 |
3,503.1 |
1,985.5 |
40.8 |
-43.3 |
|
5. Singapore |
2,911.5 |
3,938.4 |
2,712.4 |
35.3 |
-31.1 |
|
6. Thailand |
988.7 |
1,243.7 |
1,181.6 |
25.8 |
-5.0 |
|
B. Africa |
4,202.3 |
6,377.8 |
4,791.4 |
51.8 |
-24.9 |
|
of which: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. Benin |
51.8 |
82.8 |
100.5 |
60.0 |
21.3 |
|
2. Egypt Arab Republic |
786.7 |
908.3 |
794.2 |
15.4 |
-12.6 |
|
3. Kenya |
31.1 |
34.0 |
37.6 |
9.3 |
10.6 |
|
4. South Africa |
1,730.5 |
2,763.4 |
2,266.1 |
59.7 |
-18.0 |
|
5. Sudan |
142.0 |
273.8 |
128.9 |
92.8 |
-52.9 |
|
6. Tanzania |
19.1 |
20.9 |
65.2 |
9.4 |
212.0 |
|
7. Zambia |
54.9 |
45.4 |
26.3 |
-17.3 |
-42.0 |
|
C. Latin American Countries |
2,316.1 |
2,437.6 |
2,444.1 |
5.2 |
0.3 |
V. |
Others |
6,050.7 |
Neg. |
179.1 |
— |
— |
VI. |
Unspecified |
267.4 |
548.6 |
487.9 |
105.2 |
-11.1 |
Total Imports |
101,030.6 |
153,859.8 |
103,787.9 |
52.3 |
-32.5 |
P : Provisional. R : Revised. Neg.: Negligible.
Source : DGCI & S |
* Prepared in the Division of International Trade, Department of Economic Analysis and Policy. The previous issue of the article was published in RBI Bulletin, March 2010. |
 IST,
IST,






















